Build a Real-Time GPS Tracker with Raspberry Pi Pico & SIM800L: Your Complete Guide to Reliable IoT Location Tracking
A Step-by-Step Guide to Building, Integrating, and Deploying Powerful IoT Location Trackers—Ideal for Vehicles, Assets, and Real-Time Visualization
How to Build a Real-Time GPS Tracker with Raspberry Pi Pico and SIM800L GSM Module
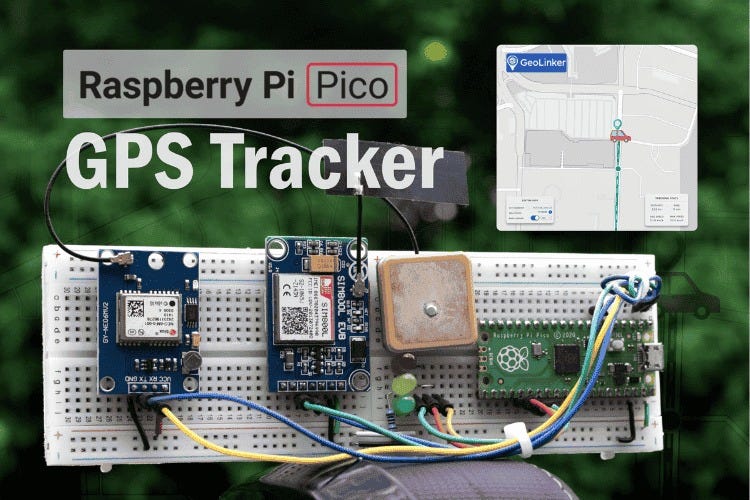
If you're searching for a game-changing way to monitor vehicles, assets, pets, or fleets anywhere in the world, you’ve landed in the right place. This in-depth guide will show you how to build a professional-grade, real-time GPS tracker using the affordable Raspberry Pi Pico, SIM800L GSM module, and Neo-6M GPS receiver. Whether you’re a hobbyist, engineer, educator, or IoT enthusiast, you’ll discover how to transmit GPS data over cellular networks, visualise it on live cloud maps, and ensure nothing is ever lost—even during network drops.
Why Choose Raspberry Pi Pico for IoT GPS Tracking?
Low Cost, High Capability: The Raspberry Pi Pico offers solid microcontroller power at a fraction of the price. Combined with SIM800L and Neo-6M modules, your complete tracker costs less than $50—making professional GPS solutions accessible to everyone.
Beginner-Friendly Hardware & Libraries: Thanks to the community-driven GeoLinker library and RP2040 board support, setting up your tracker only takes a few hours, and you can skip the tedious manual configuration steps.
Global Cellular Coverage: SIM800L works on quad-band frequencies (850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz), ensuring compatibility with 2G networks worldwide. Perfect for tracking assets anywhere.
Core Features of the DIY Raspberry Pi Pico GPS Tracker
Real-Time Location Transmission: Sends continuous, accurate position updates to the GeoLinker cloud in seconds.
Offline Data Buffering: Automatically stores GPS data locally when cellular connectivity drops; uploads buffered data as soon as the connection is restored.
Plug-and-Play Cloud Dashboard: Visualise movement on an interactive map with CircuitDigest Cloud—no complex server setup required.
Multi-Sensor Data Support: Extend tracking with battery status, temperature, humidity, driver tags, or custom payloads.
Robust Error Feedback: LED indicators (green for success, yellow for GPS errors, red for GSM issues) make hardware troubleshooting a breeze.
Cross-Platform Flexibility: Easily adapt the code for use with ESP32, Arduino, NodeMCU, or A9G modules for other tracking projects.
Step-by-Step: Build, Set Up, and Deploy Your GPS Tracker
Collect Your Components:
Raspberry Pi Pico
SIM800L GSM module (UFL/PCB/SMA antenna)
Neo-6M GPS module (active antenna recommended)
Breadboard, jumper wires
3.7V LiPo battery (>1.5A discharge), 470uF capacitor for stable power
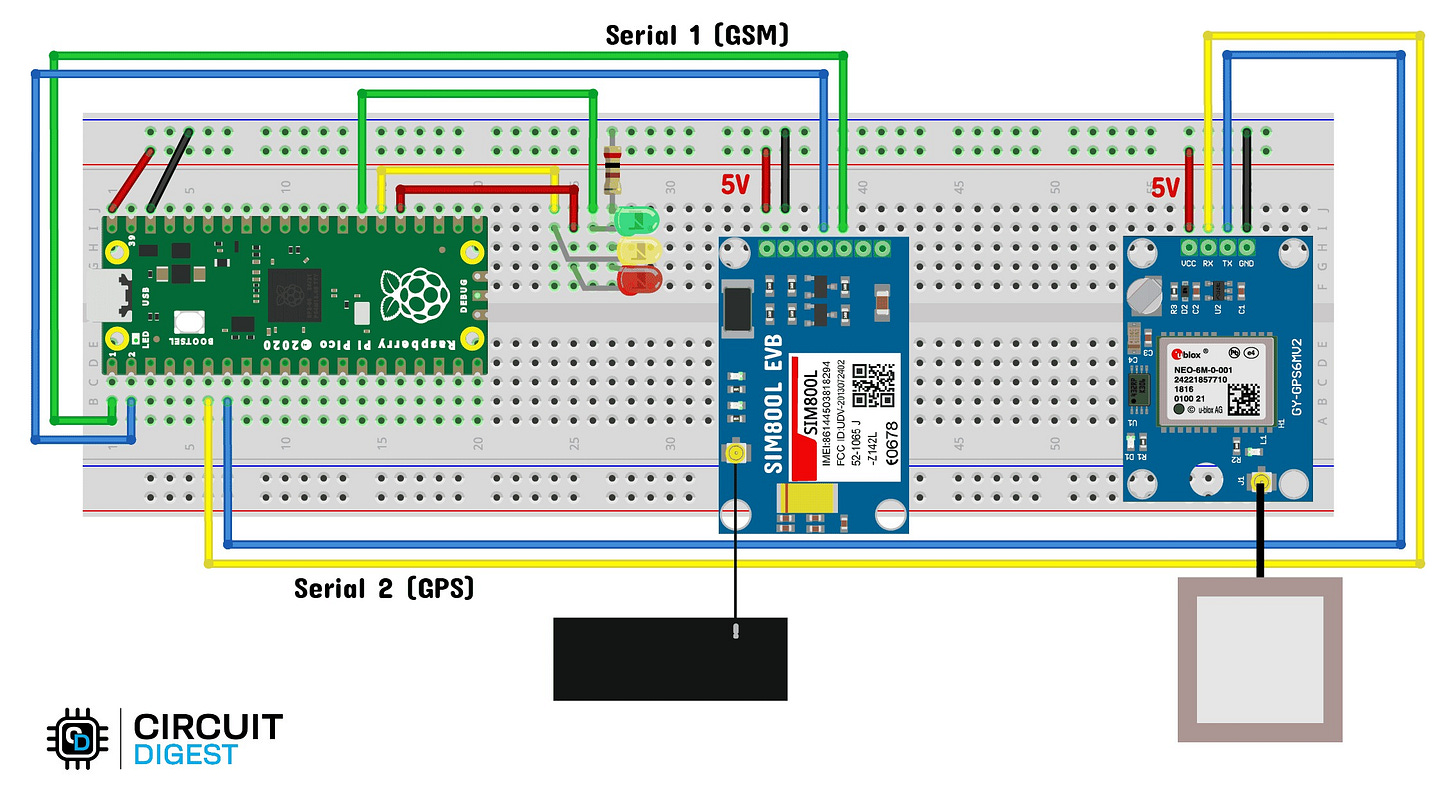
Wire Up the Circuit:
Connect Neo-6M GPS to UART1 (GPIO 4 & 5)
Connect SIM800L to UART0 (GPIO 0 & 1)
Wire status LEDs to GPIO 19, 20, and 21
Ensure common ground across modules; use a buck converter if needed
Register & Integrate with CircuitDigest Cloud:
Create your free account
Generate your GeoLinker API key (up to 10,000 GPS points per key)
Configure device ID and cloud credentials in the code
Deploy the Code:
Use Arduino IDE to install the GeoLinker library and RP2040 board support
Upload the example tracker code (shown above)
Set up cellular APN as per your SIM provider
Live Testing & Troubleshooting:
Watch real-time updates on the cloud dashboard
Verify offline storage works by simulating network loss
Use LED indicators to instantly spot hardware or network issues
Make Your Tracker Smarter: Practical Use Cases
Vehicle & Fleet Tracking: Monitor routes, stops, and status in live dashboards for delivery and logistics.
Pet & Asset Locator: Know exactly where your equipment, bikes, or pets are at all times.
Emergency/SOS Systems: Trigger instant SMS location messages for elderly care or critical alerts.
Environmental Sensing: Log location alongside temperature, humidity, or other sensor data to build advanced IoT dashboards.
Expert Tips for Reliable GPS Tracking
Power Stability Matters: SIM800L draws up to 2A peaks; use a quality battery and add capacitors to prevent resets.
Optimise Network Performance: HTTP requests on 2G can be slow; buffer data locally if speed is critical.
Antenna Positioning: Keep antenna wires away from noisy power and data lines to enhance satellite signal strength.
Getting Started Has Never Been Easier
CircuitDigest Cloud's all-in-one dashboard and APIs help you build, deploy, and scale your GPS trackers fast—no backend coding required. With open-source libraries, detailed wiring guides, and robust error handling, you’ll be tracking in real time with minimal hassle.
Whether you’re an educator teaching IoT, a small business tracking assets, or a maker building your first cloud-connected gadget, this tracker project lays the foundation for anything location-enabled. It is tailored for hobbyists, engineers, and educators looking to implement real-time location tracking in their IoT projects. Also, if you're interested in exploring more about Raspberry Pi projects, be sure to check out CircuitDigest. We have previously covered a lot of Raspberry Pi Pico and Raspberry Pi Zero Projects.